Research roundup: 2,400-year-old clay puppets; this is your brain on Klingon

The stories we almost missed this month
Also: testing the efficacy of WWI "dazzle" camouflage; how the male blue-lined octopus survives deadly mating ritual.
Credit: J. Przedwojewska-Szymańska/PASI
It's a regrettable reality that there is never time to cover all the interesting scientific stories we come across each month. In the past, we've featured year-end roundups of cool science stories we (almost) missed. This year, we're experimenting with a monthly collection of such stories. March's list includes fascinating papers on such topics as how the brain responds to speaking Klingon (or Dothraki, or Navi), the discovery of creepy preclassic Salvadoran puppets, the effectiveness of "dazzle camouflage," and how male blue-lined octopuses manage not to be cannibalized by their chosen mates.
Wind Cave’s rocks fluoresce under black light
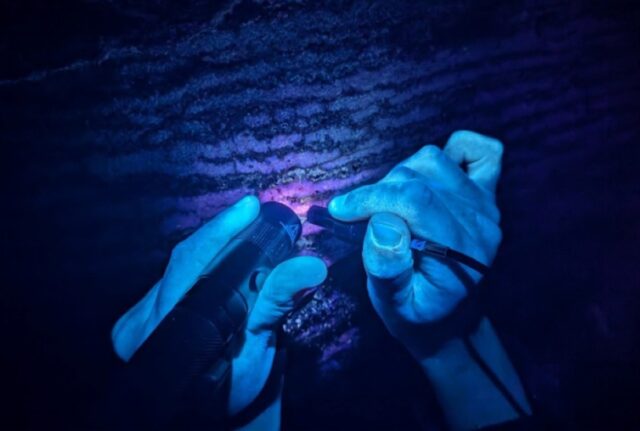

Several fluorescence measurements of a zebra calcite in Wind Cave were taken using portable spectrometers. Credit: Joshua Sebree
South Dakota's Wind Cave gets its name from the flow of air moving continually through its many passages and equalizing the atmospheric pressure between the air inside and outside—almost like the cave is "breathing." Its rock and mineral formations also boast a unique chemistry that fluoresces when exposed to black light, according to talks presented at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society in San Diego. That fluorescence could shed light on how life can thrive in extreme environments, including that of Jupiter's moon, Europa.
University of Northern Iowa astrobiologist Joshua Sebree and several students have been mapping new areas of Wind Cave (as well as other caves in the US), recording the passages, rock formations, minerals, and lifeforms they encounter in the process. They noticed that under UV light, certain parts of Wind Cave took on otherworldly hues, thanks to different concentrations of organic and inorganic fossilized chemical compounds. Those areas seem to indicate where water once flowed, carrying minerals into the cave from the surface 10,000 to 20,000 years ago, according to their analysis of the fluorescent spectra. Sebree et al. found that Wind Cave was likely carved out by waters rich in manganese, producing zebra stripes that glow pink under UV light, revealing the calcites that grew within as a result of those waters.
The physics of swing-top beer bottles
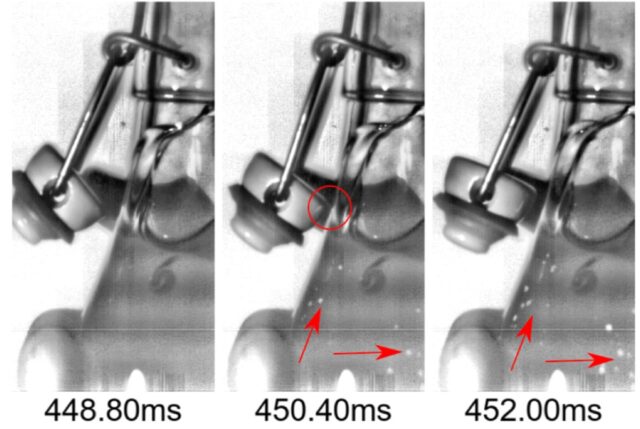
Three frames of a high-speed recording after popping a homebrewed bottle of beer. Credit: Max Koch
So-called kitchen science is all the rage these days, with champagne, wine, and beer being particularly favorite subjects for experimentation. German physicist Max Koch of the University of Goettingen is as passionate about home brewing as he is about fluid dynamics. So naturally, Koch became fascinated by the distinctive "pop and slosh" sounds produced whenever he opened one of his home-brewed swing-top beer bottles. His experiments used a high-speed camera to capture the acoustics and underlying physics, augmented by audio recording and computer simulations.
Rather than producing a single shockwave, Koch and his co-authors discovered that the unique sound occurs because popping the lid produces a vibrating standing wave, thanks to condensation within the bottleneck, according to a paper published in the journal Physics of Fluids. They were surprised to find that the frequency of the pop was significantly lower than the resonance produced by blowing across the open bottle top, which they attributed to the sudden expansion of the carbon dioxide and a strong cooling effect that reduces sound speed. The sloshing is due to the bottle's motion, and it's possible that the lid hitting the glass after popping could produce more bubbles and hence gushing.
Physics of Fluids, 2025. DOI: 10.1063/5.0248739 (About DOIs).
How effective was WWI “dazzle paint”?
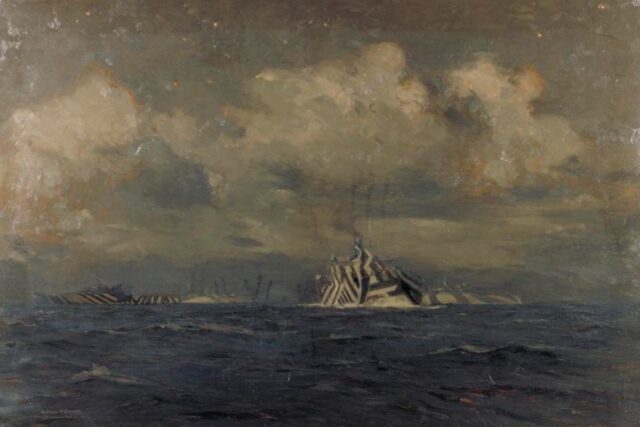

A painting by Norman Wilkinson of a moonlit convoy wearing the dazzle camouflage he invented, 1918. Credit: Public domain
During World War I, ships were often painted with complex geometric shapes in contrasting and intersecting colors, dubbed "dazzle camouflage" and usually attributed to British marine artist Norman Wilkinson. The objective was to confuse enemy U-boat captains trying to determine the speed and direction of those ships, and a 1919 study seemed to support that hypothesis. Aston University researchers have revisited that original study and concluded that the horizon effect—in which ships viewed from a distance seem to be traveling along the horizon—is a more effective means of confusing enemy combatants, according to a paper published in the journal i-Perception.
The author of the 1919 study was an MIT marine engineering student named Leo Blodgett, who painted model ships in those geometric patterns and observed them with a model periscope in a mechanical test theater to see if he could determine whether an observer's perception of the direction of travel was markedly different from the actual direction. He concluded that this was indeed the case and therefore dazzle paint was effective.
But according to the Aston scientists, Blodgett's experiment did not have a solid control condition to warrant such a conclusion. So they revisited his 105-year-old data and ran their own version of Blodgett's experiment, comparing results from his photographs showing the original dazzle camouflage with versions that had the camouflage patterns edited out. The results: the dazzle camouflage did work via a twist on perspective, but it was a small effect. The horizon effect had a much stronger confounding effect.
i-Perception, 2025. DOI: 10.1177/20416695241312316 (About DOIs).
Early Salvadoran clay puppets
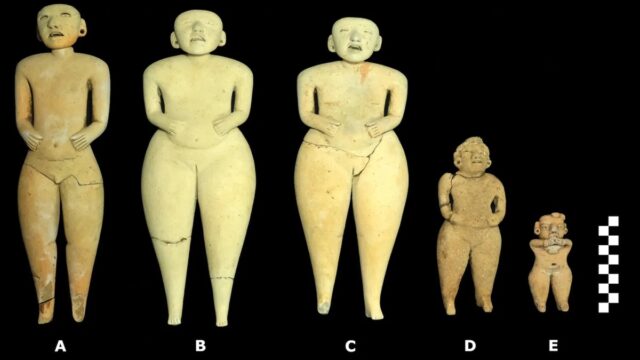
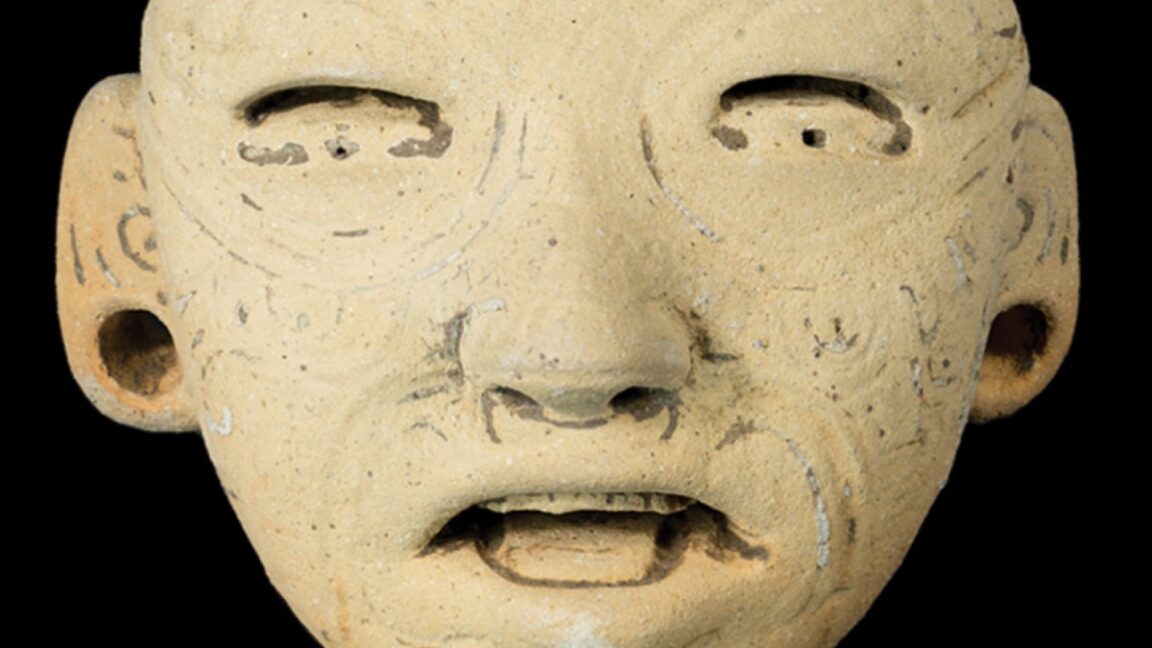
These “Bolinas” figures were found in a Salvadoran pyramid. Credit: J. Przedwojewska-Szymańska/PASI
Archaeologists excavating the San Isidro pyramid in El Salvador have discovered five carved clay figurines dating back to around 400 BCE that may have been controlled with string like modern marionettes. Such "Bolinas" figures have also been found at a Mayan burial site in Guatemala, suggesting the two areas may have shared culture and civilization, according to a paper published in the journal Antiquity.
Three of the puppets were about a foot tall, with the other two measuring about 18 centimeters. The larger ones had adjustable heads connected to their bodies via matching sockets. The carved faces feature tongues, tattoos, and facial expressions that shift depending on the viewing angle: fearful when viewed from below and grinning from above, for example. The authors suggest that these puppets weren't used as toys, but as "clay actors" in ritualistic funeral performances. "The universal impetus for creating scaled-down humanoid figures appears to be mimetic—that is, imbuing these handheld objects with deeper meanings that are readily decoded by the intended audience," they concluded, although the shared cultural "code" for interpreting those meanings has been lost.
Antiquity, 2025. DOI: 10.15184/aqy.2025.37 (About DOIs).
This is your brain on Esperanto and Klingon

Worf, son of Mogh, is surprised by new fMRI study. Credit: Paramount+
J.R.R. Tolkien invented two Elvish languages (Quenya and Sindarin) when writing The Lord of the Rings trilogy. Star Trek has Klingon, the Avatar films have Na'vi, and Game of Thrones boasts two constructed languages, or conlangs: Dothraki and High Valyrian. There are even hardcore fans who have diligently become proficient in those invented languages. And apparently conlangs activate the same parts of the brain as their native tongues, according to a paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
MIT neuroscientist Evelina Fedorenko previously spearheaded studies on how the brain responds to stimuli that share certain language features—music, gestures, facial expressions, and computer programming languages like Python. None seemed to engage the language-processing areas of the brain. Curious about what makes natural language unique, Fedorenko et al. turned to conlangs. They organized a weekend conference featuring conlang creators as speakers and invited people fluent in Esperanto, Klingon, Na'vi, Dothraki, and High Valyrian to participate. They scanned 44 conlang speakers with fMRI as they listened to sentences in both their chosen conlang and their native tongue, performing nonlinguistic tasks as a control.
The results: The same language regions lit up regardless of whether they were speaking in their chosen conlang or native natural language. This helped the group determine that language responses appear to be driven in part by how they convey meaning about the interior and exterior world—objects, properties of objects, events, etc. Python, by contrast, is highly symbolic and abstract, disconnected from the everyday "real" world we experience. The group next plans to study how the brain responds to a different conlang called Lojban, created in the 1990s, to learn more about which language features activate the brain's language centers.
PNAS, 2025. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2313473122 (About DOIs).
Venom as a protective strategy for male octopuses
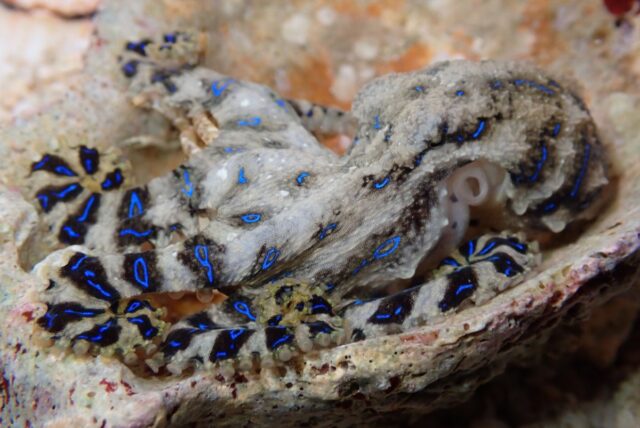

Male blue-lined octopuses inject females with venom during sex to avoid being eaten. Credit: Wen-Sung Chung/University of Queensland
Sexual cannibalism—in which a female of the species consumes the male after copulating—is a very real thing in nature, seen in insect species like mantises and spiders, certain crustaceans and gastropods, and even certain species of octopus. Case in point: the blue-lined octopus (Hapalochlaena fasciata), a tiny creature found in shallow waters whose venom can be quite deadly, especially to humans. The females of the species might be the size of golf balls, but they are nonetheless significantly larger than the males and have a tendency to eat their mates.
Fortunately, the males have developed an effective defense strategy, according to a paper published in the journal Current Biology: They inject their chosen females with tetrodotoxin (a venom also produced by pufferfish) just before mating, temporarily paralyzing the females so the males can avoid being eaten. Scientists at the University of Queensland studied the behavior of mating blue-lined octopuses in the lab and noticed that males would bite the females near the aorta as the mating ritual commenced, flooding their systems with the venom.
This immobilized the females for the duration of the mating sessions (which lasted between 40 and 75 minutes); they largely stopped breathing, turned pale, and did not respond to visual stimuli during that time. The males actually increased their respiration rate as they used a specialized mating arm to deposit their sperm into the females' oviducts to fertilize the eggs. The effects of the venom eventually wore off sufficiently for the females to push the males away without suffering any permanent effects. The authors suggest that female blue-lined octopuses may have evolved a tolerance to tetrodotoxin, ensuring they survive to lay their eggs and propagate the species.
Current Biology, 2025. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2025.01.027 (About DOIs).
Rubber hand illusion alleviates pain
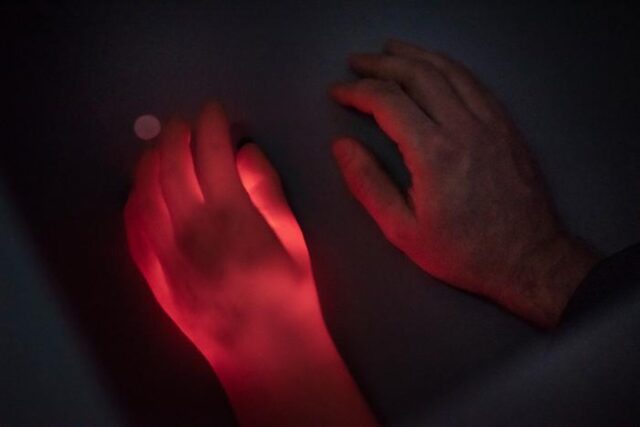
A rubber hand is perceived as part of your own body when you can't see your own. Credit: Damian Gorczany
One of the many strange things to come out of 21st-century neuroscience is the so-called rubber hand illusion, in which a subject’s hand is hidden and replaced by a rubber hand in the position where the real hand would be. When both the real and fake hands are stroked simultaneously, subjects respond as if the rubber hand were part of their body. Threaten the rubber hand by attempting to stab it with a dagger, for instance, and the participants exhibit an involuntary startle or fear response. It’s the combination of visual and tactile feedback that does it, and it only takes a few seconds for the illusion to kick in. And it's not a purely psychological effect; there have been measurable physiological responses as well.
Scientists in Bochum, Germany, have now shown that the rubber hand illusion can also alleviate pain, according to a paper published in the journal Pain Reports. They recruited 34 right-handed subjects, evaluated their individual pain thresholds, then placed the subjects' left hands behind a screen. A left rubber hand was placed in front of the subjects, which could be lit from below with red light. Then heat was applied at different temperatures to the hidden hand, while red light increased on the visible rubber hand. Subjects were asked to rate their pain in response.
The results: subjects' perception of pain decreased noticeably when the rubber hand illusion was used, compared to control conditions. The authors don't yet know what the underlying mechanism might be but suggest it could be related to visual analgesia, in which pain is considered less intense if someone can see the part of the body that is being hurt.
Pain Reports, 2025. DOI: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000001252 (About DOIs).
Jennifer is a senior writer at Ars Technica with a particular focus on where science meets culture, covering everything from physics and related interdisciplinary topics to her favorite films and TV series. Jennifer lives in Baltimore with her spouse, physicist Sean M. Carroll, and their two cats, Ariel and Caliban.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0